Dr. Rodolfo Gordigiani
Pregnancy visits in Florence
OBSTETRICS
GRAVIDANZAPRENATAL PERIOD
PREVENZIONE ONCOLOGICAPRECONCEPTION PERIOD
ButtonPREGNANCY PERIOD
ButtonPREGNANCY
Dr. Rodolfo Gordigiani is an esteemed obstetrician who has taught "Emergencies and Urgencies in Obstetrics" for over 25 years at the University of Florence. At his practices in Florence and Empoli, he conducts various tests and screenings to continuously monitor the well-being of the foetus.
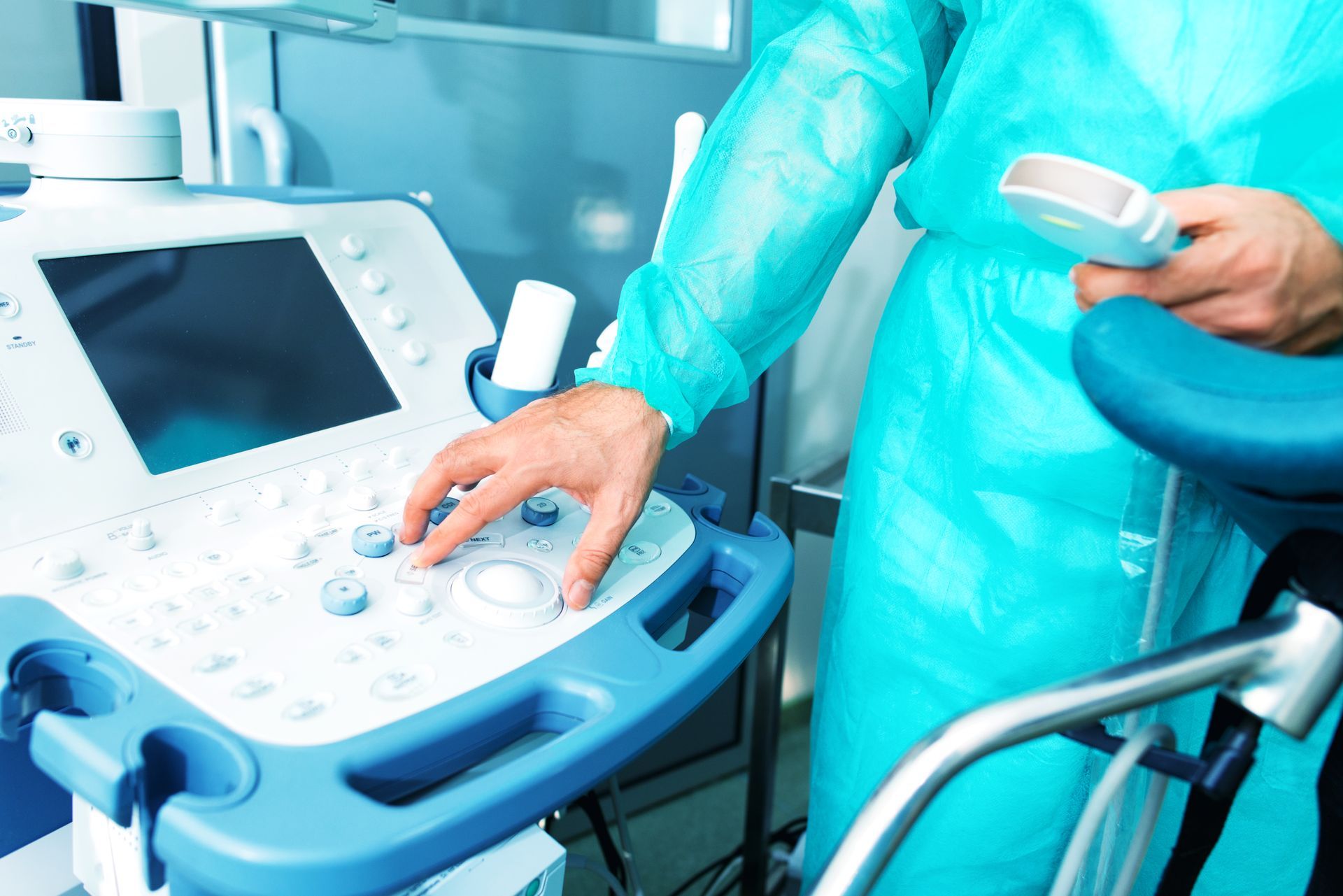
In addition to managing both normal and pathological pregnancies, Dr. Gordigiani performs obstetric ultrasounds during the first and third trimesters of pregnancy, foetal Doppler velocimetry, and prenatal diagnosis. These examinations are essential for monitoring foetal development and for early detection of any anomalies.
The first gynaecological examination in pregnancy
Dr. Gordigiani recommends undergoing a comprehensive obstetric check-up by the twelfth week of gestation.
During the initial appointment, a detailed pathological and obstetric medical history examination of the patient is conducted, considering aspects such as occupational activity, to determine whether the expectant mother's work may pose a risk to the foetus due to its strenuous nature or exposure to harmful substances.
From this initial check-up, it can be deduced whether the pregnancy is normal, meaning low risk for the foetus, or if it is pathological, meaning high risk.
Ultrasound scans during pregnancy
To verify whether the embryo is correctly positioned in the uterus and not an ectopic pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo an obstetric ultrasound in the early stages of gestation.
With this initial scan, multiple pregnancies can be identified. Additionally, the heart rate can be measured, any malformations detected, and the expected due date determined with an error margin of approximately fifteen days.
The second scan is the morphological ultrasound, which is performed between the twentieth and twenty-third week of gestation. This not only allows for the exclusion of anomalies but also provides the opportunity to measure the foetus, providing cranial and abdominal circumferences, details on the skeletal structure of the limbs, the position of the placenta, the quantity of amniotic fluid, and the gender.
Read more
The third scan is the biometric ultrasound, which is performed between the twenty-ninth and thirty-third week, during the third trimester of gestation. This allows for the assessment of foetal development based on standard values. If the values deviate significantly from the average, further detailed ultrasounds will be necessary.
Prenatal care is a fundamental aspect of pregnancy that includes healthcare, education, counselling, and resources for the mother and unborn child. It is crucial for ensuring the health and safety of both. Making an appointment for prenatal care with the attending physician as soon as pregnancy is suspected or confirmed should be a top priority. This allows for monitoring the baby's development and the mother's health, as well as identifying and managing any problems or complications as early as possible.
Prenatal period
According to the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention, a third of women who give birth develop some kind of complication during pregnancy.
Timely prenatal care is essential for identifying and managing these complications. The goal of prenatal care is to monitor the development, health, and nutritional status of both the mother and the baby. Another fundamental aspect is avoiding medications that may be harmful to the baby, as well as avoiding (unless it is an emergency) X-rays, alcohol, and smoking.
The mother should also monitor weight gain and engage in adequate physical exercise, as well as get sufficient rest.
A prenatal visit schedule is provided by the referring physician.
Typically, for a normal pregnancy, a monthly visit is advisable between the fourth and 28th week; two visits per month from the 28th to the 32nd week, then weekly visits from the 36th week until the baby is born. Patients with high-risk pregnancies, such as women aged 35 and older, diabetics, those with high blood pressure, and other chronic diseases, may schedule more frequent prenatal visits.
Preconception period
When a couple decides to plan a pregnancy, it is essential to undergo some preconception tests to assess fertility and identify any medical conditions that may interfere with conception.
Here are some tests that may be recommended:
- Blood tests: To check overall health, presence of infections or sexually transmitted diseases, hormone levels, and antibodies for diseases like rubella.
- Gynaecological examination and Pap test: To check the health of the female reproductive system.
- Semen analysis: To assess the quality of male sperm.
- Genetic testing: If there are hereditary diseases in the family, genetic testing may be useful.
- Hormonal tests: To assess ovarian function and ovarian reserve in women.
These tests are particularly important if the woman has had three consecutive miscarriages or if there are hereditary diseases in the family.
Ovulation monitoring
Ovulation monitoring involves observing the growth of the dominant follicle through a series of scheduled and personalised ultrasounds. The aim is to identify the moment of ovulation, thus allowing for targeted sexual intercourse. This process can be particularly useful for couples trying to conceive.
Sonohysterosalpingography
Hysterosalpingography is an ultrasound that assesses the patency of the Fallopian tubes and identifies or excludes any abnormalities of the uterine cavity. It is a test recommended among the assessments that women with infertility problems should undergo. The test is performed by injecting a specific contrast medium that is visible on ultrasound. The examination should be performed within the 12th day of the menstrual cycle.
It is important that the patient avoids sexual intercourse for that cycle.
Evaluation of the Fetal Karyotype in Maternal Peripheral Blood
The assessment of the karyotype on peripheral blood is an analysis that allows for the detection of chromosomal abnormalities, both numerical (such as trisomies and monosomies) and structural (such as translocations, deletions, and inversions).
Through karyotype analysis, it is possible to determine the number and structure of an individual's chromosomes, to identify or exclude any chromosomal abnormalities that may be responsible for chromosomal syndromes, intellectual disabilities, developmental delay, short stature, repeated abortions, infertility. Additionally, it allows for the diagnosis of genetic diseases, some congenital defects, and some blood and lymphatic system disorders.
Cystic Fibrosis
The test for cystic fibrosis involves searching for the main mutations in the CFTR gene, which is responsible for this condition. This is done through a simple blood sample. If mutations in this gene are detected, it may indicate that a person has cystic fibrosis or is a carrier of the disease.
PREGNANCY PERIOD
Combined Test
The combined test is a non-invasive examination that provides an estimate of the risk that the foetus may be affected by certain prenatal conditions. This test is conducted in the first trimester of pregnancy and allows for the estimation of the risk that the foetus may have a chromosomal abnormality, such as Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18), or Patau syndrome (trisomy 13). This estimate is based on the combination of maternal age with the results of blood tests and ultrasound examinations, using predefined algorithms. The examination involves a blood draw from the mother to measure two specific pregnancy-related substances (to be performed in a laboratory); and an ultrasound examination to measure the space between the skin and the spine behind the foetus's neck (nuchal translucency). For further information or to book an appointment, I recommend contacting your doctor or the relevant healthcare centre.
Morphological Ultrasound
The morphological ultrasound allows for the structural analysis of the foetus in the second trimester. Despite being a highly relevant examination capable of detecting many cases of malformations or anomalies in foetal anatomy, it is important to note that its sensitivity does not reach 100%. According to the British Society of Obstetric and Gynaecological Ultrasound, the morphological ultrasound can identify approximately 60% of malformations. Some anomalies, such as certain dilations of the urinary tract or digestive tube, or certain forms of dwarfism, may not be visible, for example, because it may still be too early for the structures in question to be fully formed. Furthermore, certain situations, such as specific conditions of maternal obesity, can make the execution of the ultrasound and the correct visualization of all foetal organs particularly challenging.
Growth Ultrasound
The growth ultrasound is performed between the 31st and 34th week of pregnancy. This examination assesses the growth and well-being of the foetus. Through various biometric measurements, the foetal growth can be compared to standard reference curves to ensure it is within expectations. This helps ensure that the foetal development is harmonious and within the normal range.
VAT No. 07253710482